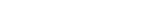Blogs
Cloud trends IT industry is rapidly evolving but you won’t know it if you see the market share of some of the big names in the industry or look at the growth. Even though there are some signs of slowdowns, revenue is still strong. There is not much to separate biggest cloud providers in terms of features as most of them offer similar feature sets but it is the little things that set one cloud vendor apart from its competitors.
With the growing popularity of generative AI, we will see its influence in the Cloud Trends industry in particular and in the technology sector in general. Cloud vendors who integrate generative AI successfully and help their users solve their biggest problems will win the race in 2024. Are you interested in learning about the future of cloud and how the cloud landscape will change in 2024? If yes, then this article is for you.
In this article, you will learn about seven cloud trends that will reshape the IT industry in 2024 and beyond.
7 Cloud Trends That Will Impact IT Industry In 2024
1. Serverless Computing
Serverless computing abstracts away infrastructure so developers only have to focus on code. Serverless platforms handle provisioning, scaling and management of the servers or containers running an application. Amazon Web Services Lambda and Azure Functions are the best examples of this.
Serverless computing enables greater agility and reduces operational costs since you only pay for the compute time used. IT teams will have less infrastructure to manage but will need skills in serverless architectures and how to monitor performance and troubleshoot issues across ephemeral workloads. Integration with existing systems can also be challenging.
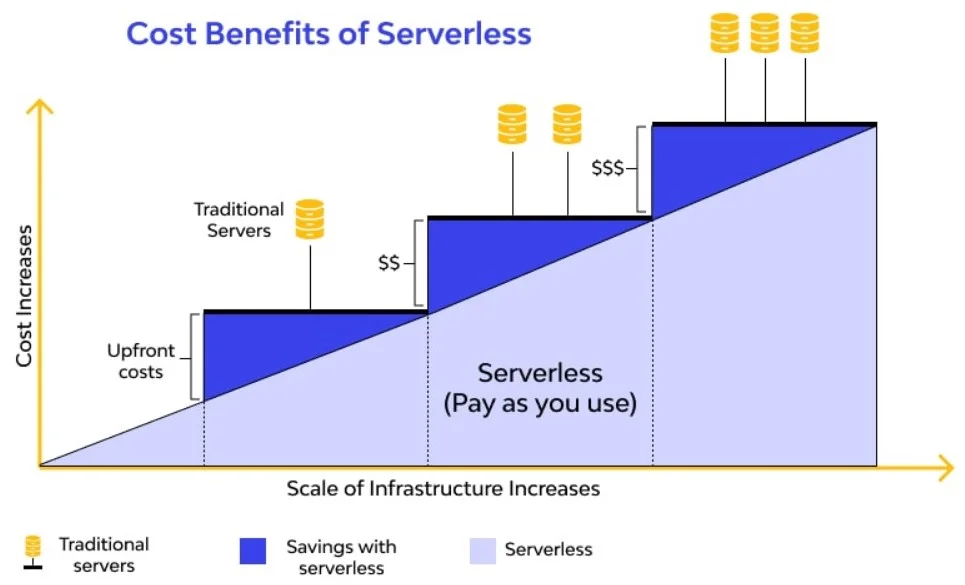
2. Edge Computing
Edge computing brings more decentralized infrastructure for processing data closer to its source. This reduces latency allowing real-time insights and actions rather than sending all data to the cloud or a data center. Examples include connected cars, smart buildings and augmented reality. Managing edge infrastructure at scale will create new complexity for IT support and operations. Teams will need skills in distributed application management and intelligent server monitoring and automation tools. Security is also a concern with data spread across more locations.
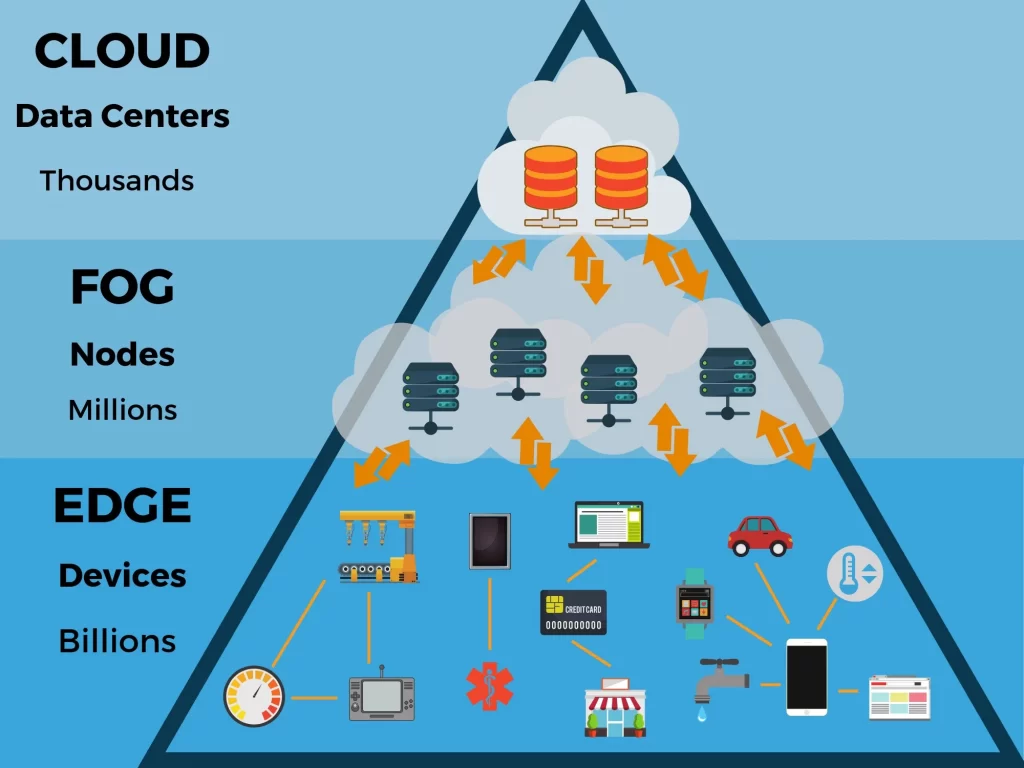
3. Cloud-Native Development
Cloud-native development using containers, microservices and orchestration engines like Kubernetes has gone mainstream. All the major cloud providers now offer managed Kubernetes services along with new tools optimized for these modern applications. The rise of cloud-native means applications are being designed from the ground up to run on the cloud and leverage its scalability. For IT, this requires new skills in cloud-native tools and a DevOps approach to work closely with app developers. Operations teams will need to manage highly distributed container environments.
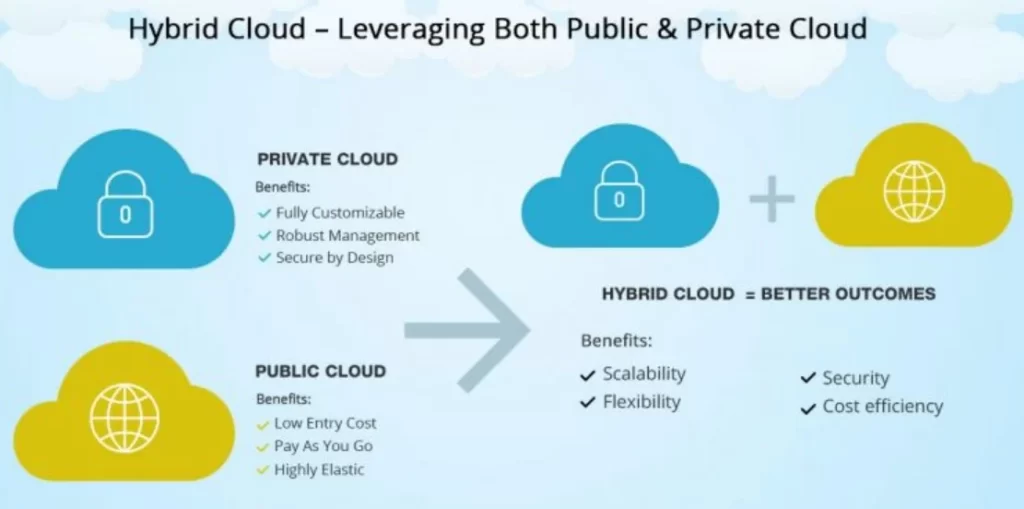
4. Hybrid Cloud
Rather than completely adopting a cloud hosting model such as private or public cloud, many enterprises are opting for a hybrid approach that keeps some applications and data on-premises while taking advantage of public cloud services. This provides the benefits of the cloud while reducing disruption and risk. IT must develop skills in bridging across the hybrid environment.
Teams will use cloud services while continuing to maintain some internal infrastructure and ensure connectivity across domains through technologies like virtual private cloud. Managing cloud security and compliance across the environments is critical.
5. FinOps
IBM sent a shockwave through the industry by raising prices for their cloud storage services by 26%. Not only that, small price hikes made their infrastructure as a service and platform as a service offering even more expensive. This might not be a one off event as other cloud vendors will also increase their prices to keep up with rising operational costs.

As cloud usage grows, managing costs is a top concern for IT and business leaders alike. It requires visibility across cloud resources and services along with governance to control spending and avoid waste. More organizations are implementing FinOps practices and tools to improve tracking and ownership of cloud costs. IT plays a key role in cost optimization but needs business partnership and engagement from application owners and users. Teams should regularly review spending and adoption to right-size workloads, shut down unused resources and leverage discounts.
6. Dedicated Cloud Infrastructure as a Service (DC IaaS)
The line between cloud server and dedicated server is blurring as cloud-style services can now be deployed in various environments like private clouds, hybrid clouds, multi-clouds, and edge locations. Terms like hybrid cloud, private cloud, multi-cloud, and edge computing reflect this phenomenon where cloud-like functionality and benefits are available across different deployment models. IDC refers to this as “Dedicated Cloud Infrastructure as a Service (DCaS)” where the cloud is seen as an operating model that can exist anywhere, not just in public cloud data centers.

Key attributes of this cloud model include scalability, elasticity, consumption-based pricing regardless of location. Cloud providers like Amazon Web Services and Microsoft now offer managed cloud services to run their cloud platforms on-premises or at edge locations. Traditional hardware vendors also offer as-a-service offerings for on-prem and edge deployments. The challenge for CIOs is managing this heterogeneous, multi-vendor environment across cloud, on-prem, and edge.
7. Industry Cloud
The emergence of generative AI has brought industry clouds back into the limelight. The speed, efficiency and flexibility offered by industry specific clouds makes them a hot favorite for business and technology professionals. Industry clouds can also help businesses make good use of limited resources to gain a competitive advantage. Healthcare, finance and technology industries are some of the biggest adopters of industrial clouds. Industries like manufacturing, energy, e-commerce and media are also jumping on the industry of cloud technology trends bandwagon.

Brian Campbell, who is a principal at Deloitte consulting said, “With the recent explosion of gen AI, executives are increasingly looking at how to use gen AI beyond proofs-of-concept, thus turning to the major providers of industry clouds, hyperscalers, independent software vendors, and systems integrators who have been quickly embedding gen AI alongside other technologies in their offerings.”
Which cloud trend will make the biggest impact in 2024? Share it with us in the comments section below.
Featured Post
Server Hardening: 10 Steps Checklist For Server Security
Server hardening is the process of securing a server by reducing its surface of vulnerability. A hardened server is resistant to attack as its potential vulnerabilities […]
Unturned Server Hosting: How to Host and Play with Friends
Table of Contents How to Play with Friends in Unturned? 1. Using Steam Friends 2. Creating a LAN Party 3. Using a Hostnoc Dedicated Server How […]
Rise Dedicated Server: Ultimate Guide to Hosting and Benefits
Table of Contents What is a Rise Dedicated Server? Benefits of Using a Rise Dedicated Server 1. Enhanced Performance: 2. Customization: 3. Scalability: 4. Improved Security: […]