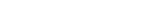Blogs

The Future of Web Hosting: Trends to Watch in 2025
September 25, 2024
10 Essential Server Hardware Components You Can’t Skip
October 11, 2024Server Operating Systems Guide: Features, Types & Best OS
Server operating systems (OS) form the critical backbone of modern IT infrastructure, providing the platform to manage hardware resources, host applications and handle multiple client requests simultaneously. Choosing the right server operating system can significantly impact your organization’s performance, security, scalability and cost-effectiveness.
This guide explores the most popular server operating systems, their key features and factors to consider when selecting the best solution for your needs.
Server operating systems (OS) form the critical backbone of modern IT infrastructure, providing the platform to manage hardware resources, host applications, and handle multiple client requests simultaneously. Choosing the right server operating system can significantly impact your organization’s performance, security, scalability, and cost-effectiveness.
In this guide, HOSTNOC explores the most popular server operating systems, their key features, and factors to consider when selecting the best solution for your needs.
- What is a Server Operating System?
- Key Features of a Server Operating System
- Types of Server Operating Systems
- How To Choose The Best Server Operating System?
- What is the Future of Server Operating Systems?
- Conclusion
What is a Server Operating System?
A server operating system is a specialized OS designed to manage server hardware and support multiple users, systems, and services simultaneously. Unlike desktop OSs, it’s optimized for performance, stability, security, scalability, and resource allocation. It includes tools for network management, user and group administration, virtualization, storage, software deployment, database hosting, remote access, load balancing, and backup, making it essential for data centers, cloud environments, web hosting, enterprise IT, and application servers.
Key Features of a Server Operating System
1. Multi-User Support
Server operating systems are built to support multiple users accessing system resources simultaneously. This feature is essential for file servers, web servers, and database servers that need to handle numerous concurrent connections without compromising performance.
2. Robust Security
Security features are a critical part of any server operating system. These include advanced firewall configurations, user authentication mechanisms, encryption, and regular security patches. Server operating systems typically offer role-based access control (RBAC) to limit user permissions and prevent unauthorized actions.
3. Remote Management
Given the nature of server operations, remote management tools are essential. Server operating systems provide robust features for remotely configuring, monitoring, and troubleshooting servers without needing physical access.
4. Virtualization Support
Many modern server operating systems support virtualization, allowing the creation and management of virtual machines (VMs). Virtualization helps businesses maximize their hardware resources by running multiple operating system instances on a single server.
5. High Availability (HA) and Redundancy
To prevent downtime, server operating systems often come with high availability features like clustering, load balancing, and failover mechanisms. These ensure continuous uptime by redistributing workloads in case of hardware or software failure.
6. Scalability
A good server operating system allows for scalability, whether it is adding more users, applications, or hardware resources. Server operating systems are designed to handle increasing workloads without degradation in performance.
Types of Server Operating Systems
1. Linux Server Operating Systems
Linux is one of the most popular and widely used server operating system platforms due to its open-source nature, flexibility, and strong community support. Linux server operating system distributions are often preferred for web hosting, databases, and cloud environments because of their performance, security, and cost-efficiency.
Popular Linux distributions:
Ubuntu Server:
Known for its ease of use and active community, Ubuntu Server is suitable for cloud infrastructure, web servers, and general-purpose use.
CentOS:
Based on Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL), CentOS provides enterprise-grade stability and security, making it ideal for large-scale deployments.
Debian:
With a focus on stability and security, Debian is a popular choice for organizations seeking long-term reliability in server operations.
Strengths of Linux:
- Open-source and free
- Highly customizable
- Excellent performance and security features
- Extensive support for open-source applications
2. Windows Server
Windows Server is developed by Microsoft and is a go-to operating system for businesses that rely on other Microsoft products like Active Directory, Exchange Server, and SharePoint. It provides an easy-to-use graphical interface and deep integration with the Microsoft ecosystem.
Key features of Windows Server
Active Directory:
Essential for managing user credentials, permissions, and policies within a domain.
Hyper-V:
Microsoft’s built-in hypervisor technology for running virtual machines.
IIS (Internet Information Services):
A web server role that makes Windows Server a popular choice for hosting websites.
PowerShell:
A command-line tool that offers extensive scripting capabilities for automation and server management.
Advantages
- Tight integration with Microsoft services and applications
- Easy-to-use interface for administrators
- Wide range of enterprise features, including Active Directory
Limitations:
– Licensing costs can be high
– Heavier on resources compared to Linux-based systems

3. macOS Server
macOS Server is Apple’s server operating system designed primarily for Mac-based environments. Though less common than Linux or Windows, macOS Server offers features like file sharing, email hosting, and web server capabilities, making it a good choice for small businesses or educational institutions that use Apple hardware. Security tools like MacKeeper can maintain system health and protect against vulnerabilities on macOS-based devices.
Core features
File sharing and backup:
Supports time machine backups and centralized file sharing.
Xsan:
A storage area network (SAN) solution for handling large-scale file systems.
Profile Manager:
Helps manage multiple Mac and iOS devices.
Strengths
- Seamless integration with macOS and iOS devices
- Simplified management for small-scale networks
Limitations:
- Limited scalability
- Fewer enterprise features compared to Windows or Linux
4. Unix-Based Systems
Unix is an older and more stable operating system known for its reliability, security, and multitasking capabilities. Though less commonly used in small businesses, Unix-based operating systems like AIX (IBM), HP-UX (Hewlett-Packard), and Solaris (Oracle) are prominent in large enterprises, particularly in industries requiring mainframe computing.
Advantages
- High stability and uptime
- Advanced security features
- Suitable for high-performance computing environments
Challenges:
- Complex to set up and maintain
- Limited community support compared to Linux
5. VMware ESXi
VMware ESXi is a bare-metal hypervisor specifically designed for virtualization. Although not a traditional operating system, it is widely used in data centers to create and manage virtual servers, enabling businesses to run multiple operating system instances on a single physical server.
Key benefits
- Exceptional performance for virtualized environments
- Supports live migration of virtual machines with minimal downtime
- Simplifies server consolidation and resource management
How To Choose The Best Server Operating System?
Here are some of the factors you should consider when choosing a server operating system
1. Workload Requirements
The choice of server operating system depends largely on the type of applications and services you intend to run. For example, Linux is typically the go-to for web servers, while Windows Server excels in environments that depend on Microsoft services.
2. Security Features
Security should be a top priority when selecting a server operating system. Look for features such as built-in firewalls, regular security patches, and strong user authentication mechanisms. Linux distributions like Debian and CentOS are known for their robust security frameworks, while Windows Server provides comprehensive security options tailored to enterprise environments.
3. Cost and Licensing
Cost considerations play a crucial role in server operating selection. Linux distributions are free and open-source, making them cost-effective. Windows Server comes with licensing fees but provides extensive enterprise support. Ensure you account for the total cost of ownership (TCO), including software, hardware, and management costs.
4. Support and Documentation
Choosing a server operating system with extensive support, either through vendor channels or community forums, is crucial for maintaining uptime. Linux distributions like Ubuntu Server offer vast community resources, while Windows Server comes with robust enterprise support packages.
5. Ease of Use
If your organization lacks seasoned IT professionals, you may want to choose a server operating system with a user-friendly interface. Windows Server’s graphical user interface makes administration relatively simple, while Linux systems often rely on command-line interfaces, which may require more technical expertise.
6. Virtualization and Cloud Support
Virtualization capabilities are essential in modern data centers. Both Linux Server and Windows Server offer native support for virtual machines. If cloud integration is a priority, many Linux distributions offer seamless cloud deployments, while Windows Server integrates tightly with Microsoft Azure.
What is the Future of Server Operating Systems?
Here are some of the ways server operating systems will evolve in the future.
1. Containerization and Microservices
Technologies like Docker and Kubernetes are revolutionizing how applications are deployed and managed. Linux distributions have a strong foothold in the containerization space, offering native support for containers and microservices architectures.
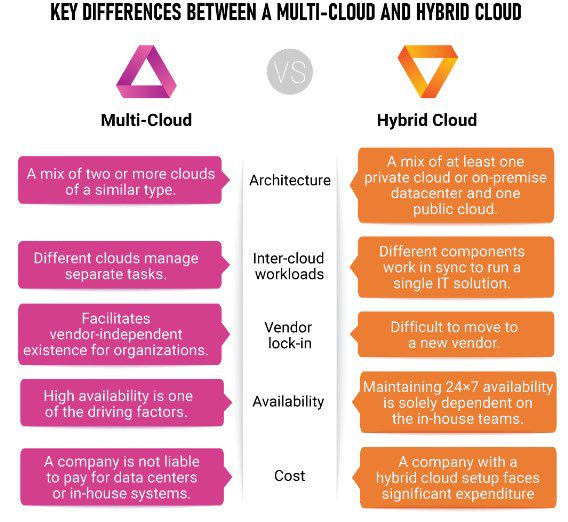
2. Hybrid and Multi-Cloud Environments
As businesses adopt hybrid cloud strategies, the demand for operating systems that offer easy cloud integration is growing. Expect more server operating system platforms to offer native tools for managing both on-premises and cloud resources.
3. Security Enhancements
With the increasing frequency of cyberattacks, security-focused server operating systems are on the rise. Expect future server operating systems to implement more advanced encryption techniques, multi-factor authentication (MFA), and automated patch management.
Conclusion
Selecting the right server operating system is a critical decision that impacts your organization’s performance, security, and scalability. Whether you choose a Linux-based operating system for its flexibility and cost-effectiveness, Windows Server for its integration with enterprise applications, or a Unix-based system for reliability, the key is aligning your choice with your specific workload and business requirements. As technology evolves, keeping an eye on trends like containerization, security, and cloud integration will ensure that your infrastructure remains future-proof.
Did this guide help you in choosing the best server operating system for your business? Share your feedback with us in the comments section below.
Muhammad Osama
Featured Post
What Is a Proxy Server? The Smart Way to Browse in 2026
Table of Contents 5 Key Takeaways What Is a Proxy Server? How Does a Proxy Server Work? What Does a Proxy Server Do? Proxy Server vs […]
What Is Localhost? Complete Guide to Master It (2026)
Table of Contents What Is Localhost? Local Hosting Definition How Localhost Works? Where is the Localhost File? Common Localhost Ports and Their Uses What Is the […]
What is Hyper-V Used For? Powerful Real-World Uses in 2026
Hyper-V is a powerful virtualization technology developed by Microsoft. It allows users to create and run virtual machines on a physical machine, making it a fundamental […]